Did you know that over 160 million patients visit urgent care centers in the U.S. each year? It’s no surprise they offer fast, affordable care when you need it most. Urgent care visits can cost 30–50% less than a trip to the ER, making them the go-to choice for non-emergency health issues.
But while patients enjoy the convenience, providers face a behind-the-scenes challenge:
Handling a complex and ever-evolving billing process that’s critical to keeping operations running smoothly.
In 2025, with new CPT code updates and evolving insurance requirements, providers must stay informed to ensure accurate billing. Billing errors account for nearly 20% of denied claims, leading to payment delays and patient dissatisfaction. Staying ahead of these changes not only protects revenue but also ensures a smoother and more reliable patient experience.
What Is Urgent Care Billing?
Urgent care billing involves documenting, coding, and submitting insurance claims for services provided at urgent care centers, which treat non-life-threatening conditions like sprains, infections, and flu symptoms.
Unlike emergency rooms or primary care practices, urgent care billing uses specific CPT codes focused on outpatient care. It excludes hospital-level complexity and long-term care management.
Key CPT Urgent Care Codes for 2025
Urgent care facilities rely on accurate and up-to-date CPT coding to ensure timely and compliant reimbursement.
In 2025, several procedural codes continue to play a central role in urgent care billing, while some have undergone updates that providers must be aware of.
Commonly Used CPT Codes in Urgent Care
The following CPT codes remain prevalent in urgent care settings due to the nature of walk-in visits and the broad scope of minor, acute treatments:
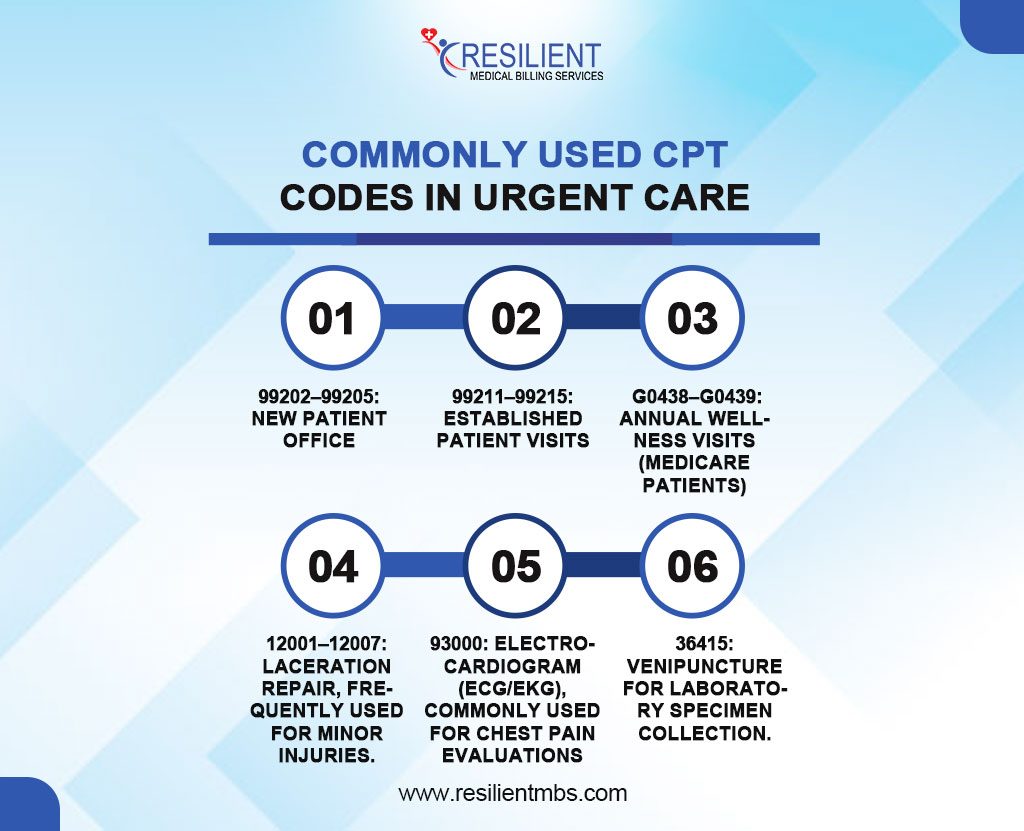
99202–99205: New patient office or other outpatient services.
99211–99215: Established patient visits.
G0438–G0439: Annual wellness visits (Medicare patients).
12001–12007: Laceration repair, frequently used for minor injuries.
93000: Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG), commonly used for chest pain evaluations.
36415: Venipuncture for laboratory specimen collection.
CPT Code S9083 – Definition and Usage
CPT code S9083 is a special code used to report global payment arrangements in urgent care billing.
Specifically:
S9083 denotes a global fee for all urgent care services provided during a single patient encounter, regardless of the number or complexity of services performed.
It is typically used when billing payers that have a flat reimbursement agreement for urgent care visits.
This code is not universally accepted and should only be used if the payer explicitly allows it under contract terms.
Updates to CPT Codes in 2025
For 2025, the American Medical Association (AMA) has released several CPT coding updates relevant to urgent care:
New Code: A new code, 99206, has been introduced to better differentiate complex new patient visits in urgent care environments.
Revised Code Descriptions: Time-based descriptors for codes 99202–99215 have been updated for clarity and alignment with E/M coding guidelines.
Deleted Codes: CPT code 99050 (services provided after hours) has been removed due to redundancy and inconsistent payer usage. Providers should consult payers for alternative documentation requirements.
Using current CPT urgent care codes provides correct documentation and reduces claim denials and compliance issues.
Common Billing Scenarios in Urgent Care
Accurate urgent care billing relies on understanding common clinical scenarios, correct CPT/ICD-10 coding, and managing bundled services.
Example Visits and Coding:
- Acute Upper Respiratory Infection
CPT: 99213 (established patient, low complexity)
ICD-10: J06.9
- Minor Laceration with Suturing
CPT: 12002 (superficial wound repair, 2.6–7.5 cm)
ICD-10: S01.81XA
- Sprained Ankle with X-Ray
CPT: 99214 (E/M), 73610 (ankle X-ray)
ICD-10: S93.401A
These cases highlight how E/M codes are often paired with diagnostic or procedural codes.
Bundled Services
Bundling occurs when services are grouped under a single CPT code or considered part of an E/M visit.
Example: Venipuncture (36415) may be bundled with lab testing.
Medicare may deny claims that “unbundle” included services.
CPT vs. ICD Codes in Urgent Care Claims
While CPT codes represent the services rendered, ICD-10 codes explain the medical necessity for those services. For a clean claim:
- CPT codes must align with the provider’s documentation.
- ICD-10 codes must support the reason for the visit and justify the procedures or diagnostics performed.
Inaccurate pairings or mismatches between CPT and ICD codes are a frequent cause of urgent care claim denials. Best practices include using automated coding systems and regular coder training to enhance billing accuracy.
Urgent Care Billing Guidelines for 2025
In 2025, as healthcare changes, the rules for urgent care bills are getting stricter. To improve revenue cycle management and cut down on claim rejections, providers need to keep up with changes to payer policies.
Payer Policies and Insurance Considerations:
Insurers, including Medicare and private payers, now require detailed documentation, precise coding, and correct place-of-service modifiers. Timely filing is critical, with some payers shortening grace periods.
Medicare and Private Insurance Requirements:
Medicare emphasizes accurate CPT coding, especially for E/M services. CPT code S9083 (global urgent care fee) requires payer agreement—many private insurers still don’t reimburse for it. Always verify payer-specific guidelines before billing.
Tips for Improving Coding and Billing for Urgent Care Services
Efficient coding and billing are vital for the financial success of urgent care centers. The right technology and skilled team can significantly boost accuracy and reimbursement speed.
Use of Billing Software and Certified Coders
AI-powered billing software ensures accurate CPT and ICD-10 coding. Hiring certified professional coders (CPCs) with urgent care expertise minimizes errors and improves claim acceptance rates.
Staff Training and Workflow Integration
Ongoing training on documentation and coding updates is essential. Integrating billing with EHR systems reduces manual errors and accelerates payment cycles.
Regular Code Audits and Updates
Quarterly or bi-annual audits help ensure compliance and uncover coding errors. Staying current with annual CPT and ICD-10 changes supports accurate billing and reduces denials.
Concluding Words
Accurate and compliant urgent care billing remains a cornerstone of operational success in 2025. Adhering to updated payer policies, ensuring staff are trained on new coding requirements, and leveraging modern billing software can significantly reduce claim rejections and improve cash flow.
It’s no longer a choice to stay up to date on revisions to the 2025 CPT and ICD-10 codes; it’s essential for long-term success. Providers need to be proactive by checking their present systems, improving their operations, and making sure they follow new billing rules.
Now is the time to strengthen your billing infrastructure. Contact Resilient MBS LLC for expert support in urgent care billing, compliance management, and coding optimization. Let our team help your practice thrive in 2025 and beyond.