As healthcare costs rise and insurance plans become more complex, self-pay in medical billing is becoming increasingly common.
More than 30 million Americans remain uninsured, and nearly 43% of insured adults are underinsured due to high deductibles and out-of-pocket expenses (Commonwealth Fund, 2023). Because of this, a lot of people are paying for their medical care without insurance, either because they have to or because they choose to.
Self-pay isn’t just a patient concern; it also presents challenges and opportunities for healthcare providers striving to ensure compliance and optimize collections.
In this blog, we’ll explore what self-pay in medical billing means, why it’s becoming more prevalent, how it compares to insurance-based billing, and best practices for managing self-paying patients effectively.
What is Self-Pay in Medical Billing?
Self-pay in medical billing refers to the payment model in which patients are directly responsible for covering the cost of their healthcare services without billing through an insurance provider. This method requires patients to pay upfront or arrange payment plans with the healthcare provider, bypassing traditional insurance claims.
Self-pay may apply to all types of medical services, including primary care, dental procedures, specialist consultations, and elective surgeries. Providers typically offer transparent pricing and may even extend discounts to self-paying patients due to reduced administrative overhead.
Differences Between Self-Pay and Insurance Billing
Understanding the difference between self-pay and insurance fee schedules is vital for both financial efficiency and regulatory compliance. Insurance billing involves multiple steps, including claim submission, eligibility verification, and handling potential denials, making the process time-consuming.
In contrast, self-pay billing is more straightforward, involving direct payments without third-party involvement. Fee structures also vary significantly; insurance companies negotiate discounted rates with providers, while self-pay patients are typically charged standard rates unless specific discounts are offered.
Payment timelines differ as well; self-pay patients often pay upfront or through structured payment plans, whereas insurance reimbursements are delayed due to claims processing.
While self-pay billing is generally less complex, it still requires accurate and transparent documentation, unlike insurance billing, which demands strict coding and adherence to payer guidelines.
Who Are Self-Paying Patients?
Self-paying patients are individuals who take full financial responsibility for their healthcare services without the involvement of a third-party payer such as private insurance, Medicare, or Medicaid. These patients pay out of pocket for their medical expenses either by choice or due to circumstances that exclude them from traditional insurance coverage.
There are several reasons why a patient might fall under the self-pay category:

- Uninsured Status: Some individuals do not have health insurance due to affordability issues, lack of access, or personal choice.
- High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs): Even insured patients may opt to self-pay if they have not yet met their high deductibles and must cover initial costs themselves.
- Out-of-Network Care: Patients who choose providers not covered under their insurance network often must pay out of pocket.
- Non-Covered Services: Certain medical services, elective procedures, or alternative therapies may not be included in insurance plans, prompting patients to self-pay.
- Immigration or Residency Status: Non-residents or individuals with temporary immigration status may not qualify for public or private insurance programs.
Self-Pay vs Insurance Fee Schedules
Self-Pay vs. Insured Patient Charges
Healthcare providers often charge self-paying patients based on their standard fee schedule, which is typically higher than the discounted rates negotiated with insurance companies.
Negotiated Rates vs. Full Fee Schedule
Insured patients benefit from pre-negotiated rates, often 20% to 80% less than standard charges. Self-paying patients may face full fees unless providers offer discounts, financial aid, or a separate fee schedule.
The Need for Transparent Pricing
Transparent pricing helps self-paying patients make informed choices. Many providers now offer upfront cost estimates, sliding fee scales, and public price lists to promote fairness and trust.t
Rules for Charging Self-Pay Patients
Charging self-pay patients requires strict adherence to legal, ethical, and regulatory standards. Providers must ensure their billing practices are transparent, fair, and compliant.
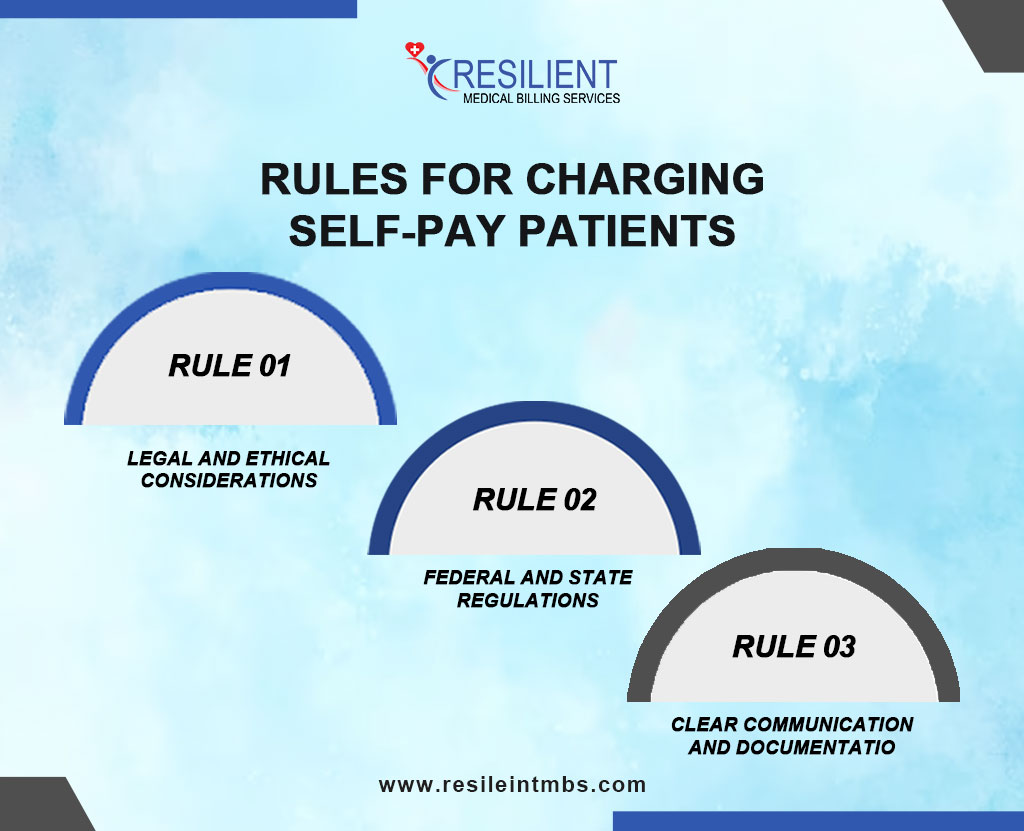
- Legal and Ethical Considerations
Providers have an ethical duty to treat all patients fairly. Charging self-pay patients more than insured rates—without clear justification—can lead to disputes and damage trust. Ethical billing includes offering financial counseling, discounts, or payment plans when needed.
- Federal and State Regulations
Laws like the No Surprises Act protect self-pay patients from unexpected bills, especially in emergency or out-of-network situations. Patients must receive a Good Faith Estimate (GFE) outlining expected costs before care. States may also impose additional transparency and pricing rules.
- Clear Communication and Documentation
Providers should discuss charges upfront and document financial agreements, including service scope, costs, payment timelines, and assistance options. Clear communication and written consent help prevent disputes and build patient trust
What is Self-Pay Insurance?
Self-pay insurance is not always what it sounds like. For actual individuals, self-pay means that the patient pays for their medical bills without using a standard insurance plan. So, self-pay is not a type of insurance. It is a way of paying for medical care where the patient is responsible for all costs.
Benefits and Challenges of Self-Pay in Healthcare
Pros: Faster Payments, Less Admin Work
Self-pay simplifies the revenue cycle by eliminating third-party payers. Providers often receive payment at the time of service, avoiding delays from claims and pre-authorizations. It also gives providers more control over rates and payment policies.
Cons: Financial Burden on Patients, Collection Challenges for Providers
Patients may struggle with high out-of-pocket costs, leading to delayed care. For providers, direct collections can be difficult and time-consuming, with a greater risk of unpaid bills.
Strategies for Managing Self-Pay Patients Effectively
Providers should take preventative steps like:
- Discounts or sliding scales for quick payments.
- Give precise Good Faith Estimates to minimize confusion.
- Create explicit payment arrangements and financial aid initiatives.
- Billing policy communication training for front office staff.
Best Practices for Managing Self-Paying Patients
Managing self-pay patients requires a balanced approach that combines financial responsibility with compassionate care.
The following best practices help improve patient satisfaction, increase collections, and ensure compliance:
Offer Payment Plans and Financial Counseling
Provide flexible, interest-free payment plans to ease the financial burden. Offer financial counseling to help patients understand payment options, explore assistance programs, and manage healthcare costs.
Use Technology for Upfront Estimates
Leverage practice management software or patient portals to give accurate cost estimates before care. These tools promote transparency, build trust, and help patients plan financially.
Train Staff and Standardize Billing Policies
Train front-desk and billing staff to communicate clearly and professionally. Use consistent billing policies to reduce errors, ensure fairness, and enhance the overall patient experience.
Final Words
As healthcare costs continue to rise, the number of self-paying patients is steadily increasing. To serve this growing population, providers must adopt transparent, ethical, and efficient billing practices.
The key to success lies in balancing compliance, clarity, and compassionate care.
Is your practice ready to handle the difficulties that come with self-pay patients? Resilient MBS LLC focuses on making billing easier, putting patient-centered procedures in place, and making sure that all rules are followed.
Contact Resilient MBS LLC today to discover how our expert solutions can improve your revenue cycle and elevate the patient experience.