Understanding primary vs secondary insurance coverage is essential for every healthcare provider who wants to avoid claim denials, reduce billing delays, and improve cash flow. With more patients now carrying dual health insurance coverage, determining which plan pays first has become a daily operational challenge.
Incorrect coordination of benefits (COB) directly leads to rejected claims, delayed reimbursements, compliance risks, and frustrated patients. This complete guide explains primary and secondary health insurance rules, including Medicare primary vs secondary, and shows providers exactly how to manage dual insurance correctly from verification to payment posting.
What Is Primary vs Secondary Insurance Coverage?
Primary vs secondary insurance coverage defines the order in which multiple insurance plans pay for a patient’s medical services.
- Primary insurance pays the claim first based on its contracted rates and coverage rules.
- Secondary health insurance pays after the primary and may cover remaining deductibles, coinsurance, or non-covered services.
This system is governed by coordination of benefits (COB), a process designed to prevent duplicate payments and ensure proper payer sequencing.
In simple terms:
- Primary = First payer
- Secondary = Second payer
For providers, understanding this order is critical for clean claim submission.
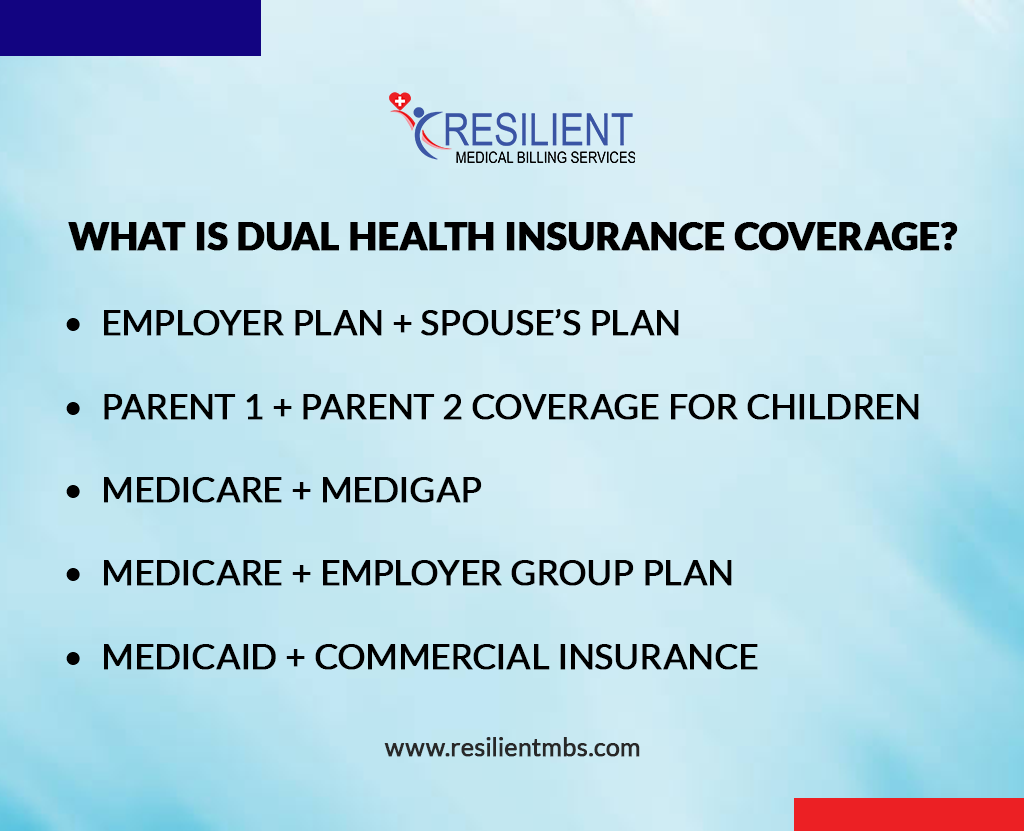
What Is Dual Health Insurance Coverage?
A patient has dual health insurance coverage when two active insurance plans exist simultaneously. This is now extremely common due to:
- Employer plan + Spouse’s plan
- Parent 1 + Parent 2 coverage for children
- Medicare + Medigap
- Medicare + Employer group plan
- Medicaid + Commercial insurance
Each scenario follows specific dual health insurance coverage rules, and billing must strictly follow the correct order.
How to Determine Primary vs Secondary Insurance (Golden Rules)
Providers use standardized rules to determine the correct payer order:
Birthday Rule
For dependents covered by both parents, the parent whose birthday appears first in the calendar year provides primary coverage.
Employment Rule
Active employee coverage always pays before retiree or COBRA plans.
Court Orders
If a legal document assigns coverage responsibility, that plan becomes primary.
Medicaid Rule
Medicaid is always the payer of last resort.
Workers’ Compensation and Liability
- Work injuries → Workers’ comp is primary
- Auto accidents → Liability insurance is primary
Following these rules prevents payer conflicts and denials.
Medicare Primary vs Secondary Insurance: Provider Guide
Medicare coordination errors are one of the biggest sources of overpayments and audits.
When Medicare Is Primary
- Patient is 65+ with a small employer plan (<20 employees)
- Retired patients with COBRA or retiree insurance
- ESRD after the 30-month coordination period
When Medicare Is Secondary
- Patient is 65+ with a large employer plan (20+ employees)
- Disability cases with employer groups of 100+ employees
- ESRD during the first 30 months of employer coverage
Understanding Medicare primary vs secondary rules protects both compliance and reimbursement.
Why Secondary Health Insurance Is Important for Revenue
Many providers fail to bill secondary payers properly, causing:
- Uncollected deductibles
- Increased patient balances
- Lost reimbursements
Secondary health insurance often covers:
- Copays
- Deductibles
- Coinsurance
- Non-covered services (depending on policy)
Proper dual billing reduces patient financial burden and increases total collections.
How Providers Should Verify Primary and Secondary Insurance
Accurate verification must happen at every visit:
Front Desk Collection
- All insurance cards
- Policyholder names
- Employer details
- Medicare ID
- Disability or ESRD status
Electronic Eligibility Checks
- Active coverage dates
- Plan type and payer priority
- Copays and deductibles
COB Confirmation
- Verify which plan is primary
- Confirm effective dates
- Document employer size
Failure at this stage creates billing chaos later.
Common Mistakes in Primary vs Secondary Billing
The most frequent provider errors include:
- Billing secondary before primary
- Using outdated COB data
- Assuming Medicare is always primary
- Ignoring secondary insurance entirely
- Incorrect employer size assumptions
Financial Impact
- Claim denials
- Increased AR
- Patient disputes
- Audit risks
Correct payer sequencing eliminates these losses.
Best Practices for Managing Dual Health Insurance
To fully control primary and secondary health insurance workflows, providers should:
- Use automated eligibility verification software
- Train staff on payer sequencing rules
- Perform routine COB audits
- Educate patients on their insurance orders
- Ensure claims are released only after the primary EOB posting
Strong workflows equal clean claims and faster cash flow.
Why Primary vs Secondary Insurance Accuracy Impacts Compliance
Wrong payer billing can trigger:
- Medicare overpayment audits
- Medicaid compliance penalties
- Contract violations with commercial payers
Accurate COB protects:
- Legal standing
- Payer relationships
- Long-term reimbursement stability
How Resilient MBS Helps Providers Fix COB and Insurance Errors
Managing primary vs secondary insurance coverage in-house is complex and time-consuming. Resilient MBS provides expert support with:
- Insurance verification & COB setup
- Medicare primary vs secondary compliance
- Dual coverage claim processing
- Denial prevention & claim corrections
- Revenue cycle optimization
- Fewer denials
- Faster reimbursements
- Lower patient balances
- Stronger compliance
Contact Resilient MBS today to eliminate COB errors and stabilize your revenue cycle.
Final Thoughts
Mastering primary vs secondary insurance coverage is no longer optional for healthcare providers. With rising dual health insurance coverage, providers must understand secondary health insurance, Medicare primary vs secondary, and all coordination of benefits rules.
When implemented correctly, accurate payer sequencing:
- Reduces claim denials
- Speeds reimbursement
- Improves patient satisfaction
- Protects compliance
And when handled by experts like Resilient MBS, it becomes a revenue protection system rather than a billing burden.
Resilient MBS helps healthcare providers eliminate COB errors, improve insurance verification accuracy, and optimize revenue cycle performance with expert billing support.
FAQs
How do I know which insurance is primary or secondary?
Follow the coordination of benefits rules. The insurance that pays first is primary; the other is secondary.
Can a patient have both primary and secondary insurance?
Yes. Patients often have employer plans, spouse coverage, Medicare, Medicaid, or supplemental policies together.
When is Medicare primary?
Medicare is primary for retirees, small employer plans, Medigap coverage, and certain ESRD cases.
What happens if I bill the secondary insurance first?
The claim will be denied. The primary must always process the claim first.
Should providers verify insurance at every visit?
Yes. Insurance coverage and payer orders can change at any time.