The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) helps to facilitate communication between patient, healthcare provider and insurance company regarding billing and record keeping. 50 years back in 1966, AMA created CPT codes that have become the most popular tool to code bills in the medical field in the United States.
While CPT codes contain more than 10,000 various numbers, the constant usage rates are done by over a thousand numbers. Medical billing errors run to $68 billion annually in the United States, hence the significance of accurate CPT codes. Lab CPT codes help to define individual laboratory procedures. It also means that the healthcare workers and insurance firms carry out their paperwork, bills, etc. and all of these save time and costs leading to higher lab service reimbursements.
Lab CPT codes are essential for effective and accurate medical billing and record-keeping, as we’ll discuss in this blog. We’ll explain lab CPT codes, how they categorize and streamline laboratory tests, and why healthcare providers and insurance companies need them. Understanding lab CPT codes helps simplify medical billing for providers, patients, and billers.
What Are Lab CPT Codes?
Lab CPT codes are as a result specific to laboratory services. These codes refer to blood tests, pathology tests and other samples necessary to diagnose a patient’s overall health. Lab CPT codes make billing and patient records accurate.
The following codes keep billing complications away, and set down legitimate charges and full records in general healthcare practices. These standardized codes assist healthcare practitioners in avoiding the errors often caused by billing issues, discourage denials of charges, and maintain full records in healthcare practices for quality medical practices.
Common CPT Codes for Laboratory Services
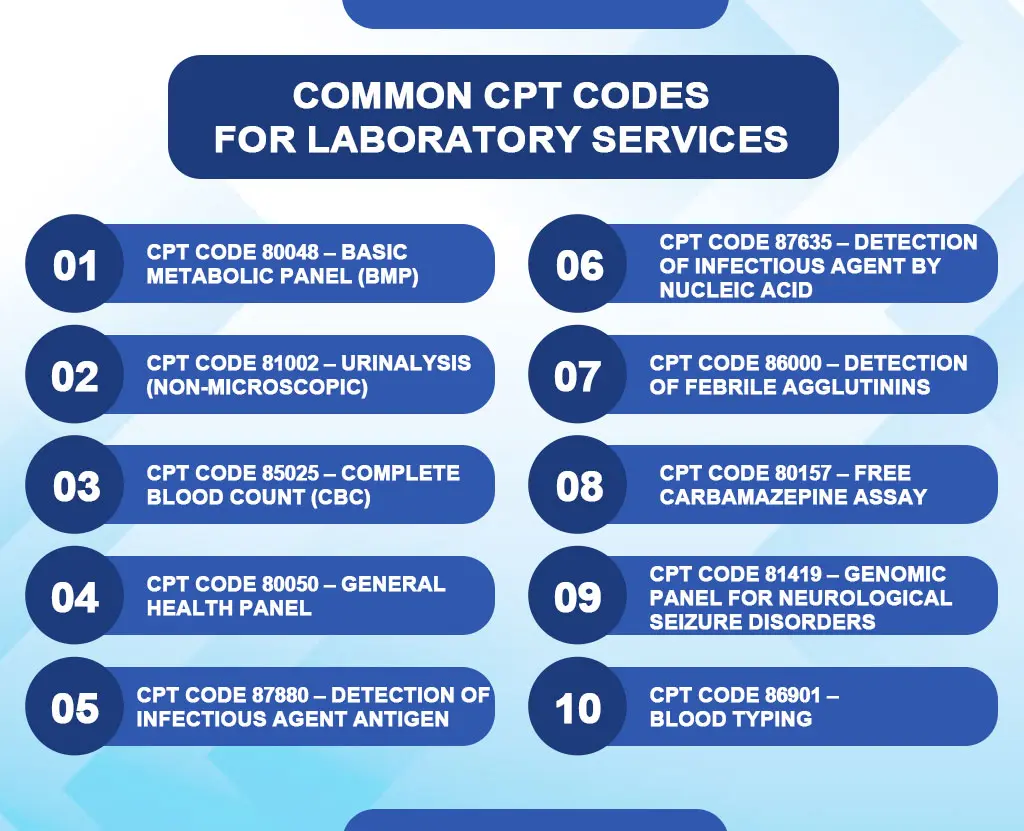
Here is a summary of frequently used CPT codes for laboratory services:
CPT Code 80048 – Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP)
This code applies when a BMP test is ordered, typically in emergencies, to provide essential information on a patient’s metabolism and kidney function.
This code measures eight specific blood chemicals: creatinine, sodium, calcium, chloride, potassium, carbon dioxide, blood urea nitrogen, and glucose.
CPT Code 81002 – Urinalysis (Non-Microscopic)
Used for various screenings, including pre-surgical evaluations, pregnancy, or routine exams, this code represents a urinalysis test without microscopic examination.
A urine sample is collected, and the lab analyst uses a dipstick or reagent tablet to obtain results within a set time. No microscopic analysis is involved.
CPT Code 85025 – Complete Blood Count (CBC)
This CPT code is used for a CBC test, which is useful for identifying conditions like anemia or detecting significant drops in white blood cells, potentially indicating infections like dengue.
A blood sample is taken and stored in a tube with anticoagulants. Automated analyzers then quantify different blood cell types.
CPT Code 80050 – General Health Panel
This CPT code is used for a general health panel with a specific clinical test set. It should be billed only if the provider explicitly requests a comprehensive health screening, as using it for diagnostic component tests may lead to claim rejections.
CPT Code 87880 – Detection of Infectious Agent Antigen
This code is used for rapid antigen testing to detect infectious agents in a patient sample, such as group A Streptococcus, usually from a throat swab. It allows for a quick diagnosis of certain infections.
CPT Code 87635 – Detection of Infectious Agent by Nucleic Acid
Similar to code 87880, this code uses a nucleic acid amplification method to detect infectious agents like SARS-CoV-2. Widely used during the COVID-19 pandemic, it remains relevant for detecting viral infections.
CPT Code 86000 – Detection of Febrile Agglutinins
This code represents qualitative or semiquantitative immunoassays for febrile agglutinins in blood, useful for diagnosing illnesses like Q fever, typhus, or brucellosis.
CPT Code 80157 – Free Carbamazepine Assay
This test measures free (unbound) carbamazepine levels in the blood, often used to monitor medication levels for psychiatric or neurological conditions like epilepsy.
CPT Code 81419 – Genomic Panel for Neurological Seizure Disorders
This code is used for a genomic sequencing panel that analyzes at least 24 genes to assess genetic risk factors for epilepsy and related neurological seizure disorders.
CPT Code 86901 – Blood Typing
Found within transfusion medicine, this code covers blood typing for the Rh blood group, typically using serum plasma as the sample.
Lab Code vs. CPT Code: What’s the Difference?
Lab codes and CPT codes are important in medical billing and coding, although they are utilized differently. Laboratory codes identify each test or treatment performed in a lab. They expedite lab, healthcare provider, and insurance company communication to standardize test codes for invoicing and record-keeping.
In contrast, CPT codes cover a wider range of medical treatments, including diagnostic, therapeutic, and surgical procedures. CPT codes, developed by the American Medical Association (AMA), standardize healthcare billing across specializations and facilities. Complex lab tests may employ CPT codes, whereas lab codes are particular to individual tests.
It is very important to know the difference between lab and CPT codes for correct billing and compliance, as using the wrong code can cause insurance claims to be delayed or denied. CPT codes cover a lot of different services, but lab codes are special to the lab. Choosing the right code is very important for making sure that billing rules are followed.
The Role of CPT Code Lab Review in Medical Billing
Efficiency in coding and following legal accountability need code lab reviews of CPT. Test CPT codes are required to ensure that a proper code corresponding to services and payer requirements is allocated to laboratory services. Mistakes cause claims rejection, delayed payments, or penalties that compelling checks are required in lab billing.
The procedure of CPT code lab review includes the examination of paperwork, lab reports, and CPT code entries to identify discrepancies. Recommendations for this evaluation include verification of codes with lab personnel and comparing the service descriptions and current coding references. It can also accelerate acceptance if codes match payer requirements.
Healthcare providers can reduce insurance claim rejections due to coding errors by employing a comprehensive CPT code lab check. This improves cash flow, patient satisfaction, and lab compliance with healthcare laws.
Final Words!
Lab CPT codes start from 47501 up to 50606 while Laboratory CPT codes range from 80047- 89398; this has made coding a difficult nightmare for lab technicians, let alone the referrer prescribers. With the list of most frequent lab CPT codes, we could explain some of the coding rules for different laboratory and pathology services.
In medical billing and coding laboratories Current Procedural Terminology codes are also known as lab CPT Codes play a vital role in identifying accurate reimbursement and conformity. These codes describe laboratory services as per their requirements for claims filing and avoid delays or denials in them.
To get a more accurate code application and get help with your revenue, consult with coding specialists or use a dedicated billing service such as Resilient MBS as your automated billing system. Get in touch with Resilient MBS now to know more about our medical billing services.