Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are among the most frequently diagnosed bacterial infections globally, affecting over 150 million individuals annually. In the United States, they lead to more than 8 million doctor visits every year. These infections, ranging from mild bladder infections to serious kidney complications, often result in discomfort, missed workdays, and increased healthcare expenses.
From a medical billing perspective, using the correct ICD-10 code for urinary tract infection (UTI) is essential. It ensures that providers get reimbursed promptly, claims are not denied, and the diagnosis accurately reflects patient conditions.
In this article, we’ll explain the ICD-10 for urinary tract infection, outline the most common codes, share documentation best practices, and show how accurate coding supports better reimbursement outcomes for healthcare providers.
Understanding ICD-10 Coding for UTIs
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10), is a universal coding system used to classify medical conditions and procedures. Each ICD-10 code identifies a specific disease or disorder, providing clarity for healthcare documentation and insurance processing.
In the case of urinary tract infections, ICD-10 codes define the type, site, and severity of infection, such as the bladder, kidneys, or urethra. Correct coding ensures that medical claims reflect accurate diagnoses, minimizing errors and delays in claim processing.
Incorrect or vague coding can result in claim denials, underpayments, and audit risks, ultimately affecting the practice’s financial performance.
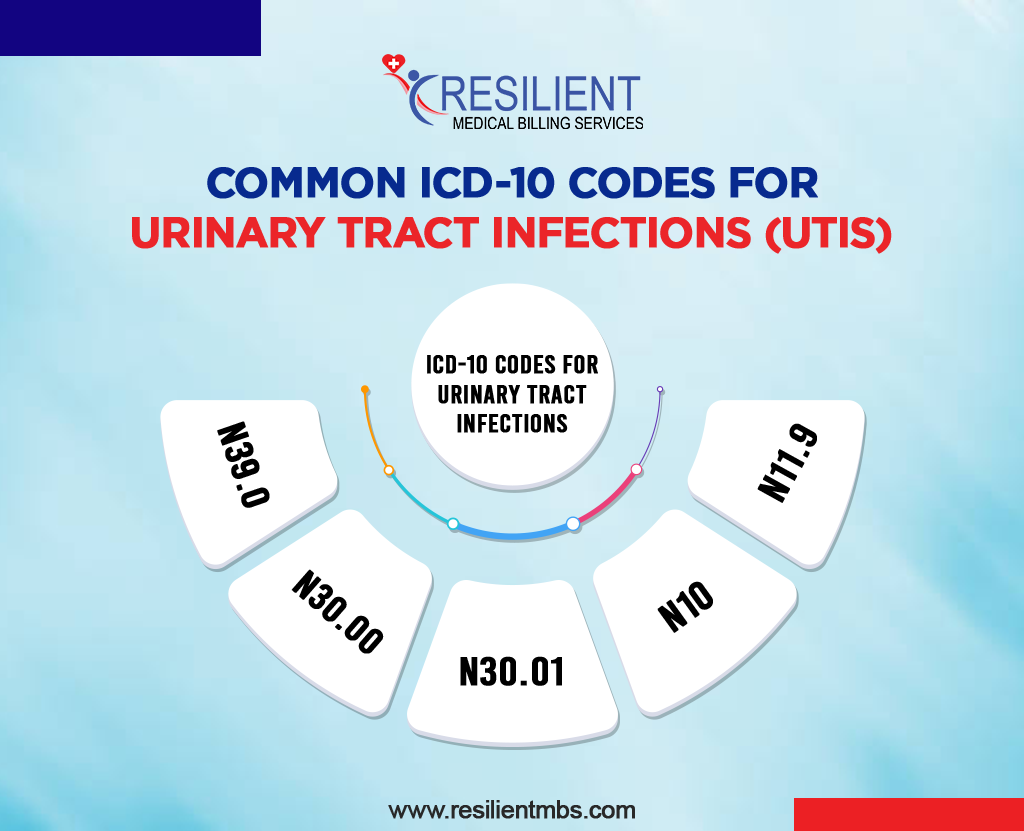
Common ICD-10 Codes for Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Here are the most commonly used ICD-10 codes for urinary tract infections that billers and coders must know:
| ICD-10 Code | Description |
| N39.0 | Urinary tract infection, site not specified, is used when the specific site of infection is not documented. |
| N30.00 | Acute cystitis without hematuria, sudden bladder infection without blood in the urine. |
| N30.01 | Acute cystitis with hematuria, bladder infection accompanied by blood in the urine. |
| N10 | Acute pyelonephritis, a kidney infection characterized by fever, flank pain, and urinary symptoms. |
| N11.9 | Chronic pyelonephritis, unspecified, recurring or long-term kidney infection not specified further. |
Documentation Tip:
Always document the exact site of infection and any associated symptoms. Avoid using N39.0 if more specific details are available; specificity strengthens claim accuracy.
ICD-10 Coding Examples and Documentation Guidance
Accurate urinary tract infection ICD-10 coding begins with precise documentation from the provider. Each diagnosis should clearly describe the location, cause, and symptoms of the infection.
Coding Examples
Example 1:
For a lower UTI caused by E. coli, use N39.0 (UTI, site not specified) and B96.20 (Unspecified E. coli as the cause of disease).
Example 2:
If a patient has acute cystitis without hematuria, N30.00. If hematuria is present, code N30.01.
Example 3:
For acute kidney infection, use N10 (Acute Pyelonephritis).
Documentation Best Practices:
- Specify infection site (bladder, kidney, or urethra).
- Record organism, such as E. coli or Klebsiella.
- Note symptoms, like fever, dysuria (burning urination), or hematuria.
- Avoid vague documentation to prevent underpayment or denials.
Related ICD-10 Codes for Associated Conditions
UTIs often occur alongside other conditions. Reporting related ICD-10 codes ensures a complete clinical picture and supports higher reimbursement accuracy.
- Sepsis ICD-10 (A41.9) — used when a severe UTI progresses to sepsis.
- ICD-10 Anemia (D64.9) — for patients with anemia linked to chronic infection.
- Pregnancy-related or catheter-associated infections should also be documented as applicable.
How Accurate ICD-10 Coding Affects Reimbursement
Using the correct ICD-10 codes for urinary tract infection directly influences your practice’s revenue cycle. Insurers rely on precise codes to determine medical necessity and approve payment quickly.
Key Benefits of Accurate Coding:
- Fewer Claim Denials: Proper documentation prevents billing rejections and delays.
Compliance with Payer Rules: Accurate codes meet CMS and private insurer standards. - Improved Cash Flow: Timely payments enhance overall financial stability.
Accurate ICD-10 coding also supports data-driven decision-making, allowing healthcare organizations to track infection trends and enhance care outcomes.
Best Practices for Medical Billers and Coders
To maintain accuracy and compliance, billers and coders should adopt the following strategies:
1. Stay Updated on Code Changes
ICD-10 codes are revised annually. Regularly reviewing CDC and CMS updates helps prevent outdated coding errors.
2. Prioritize Ongoing Training
Periodic training ensures coding teams remain proficient, minimizing errors that lead to denied claims.
3. Conduct Regular Billing Audits
Routine audits identify inaccuracies early, ensuring every claim aligns with documentation.
4. Collaborate with Certified Coders
Certified coders bring expertise in complex or recurring UTI cases, leading to better accuracy and quicker reimbursement.
Conclusion
Accurate ICD-10 coding for urinary tract infections is critical for correct diagnosis reporting, smooth insurance processing, and maintaining regulatory compliance. With detailed documentation and the right coding practices, healthcare providers can reduce denials, improve patient care, and enhance overall reimbursement efficiency.
Struggling with denied claims or slow reimbursements?
Let Resilient MBS handle your coding and billing challenges. Our certified experts simplify the process, ensuring every claim is coded accurately for maximum reimbursement.
Contact Resilient MBS Today to boost your ICD-10 accuracy, strengthen your revenue cycle, and eliminate billing stress.
FAQs
What is the ICD-10 code for urinary tract infection?
The ICD-10 code for UTI is N39.0, used when the infection site is not specified.
Which ICD-10 codes apply to specific UTI types?
For acute cystitis, use N30.00 (without hematuria) or N30.01 (with hematuria). For kidney infections, use N10.
Can UTIs cause other conditions in coding?
Yes. UTIs can lead to sepsis (A41.9) or anemia (D64.9) in chronic cases. Always code related conditions for complete documentation.
Why does ICD-10 accuracy matter for reimbursement?
Accurate coding prevents claim denials, ensures proper payment, and maintains compliance with CMS and payer guidelines.
How can medical billers improve coding accuracy?
By staying updated on ICD-10 changes, using precise documentation, and collaborating with certified medical billing professionals like Resilient MBS.